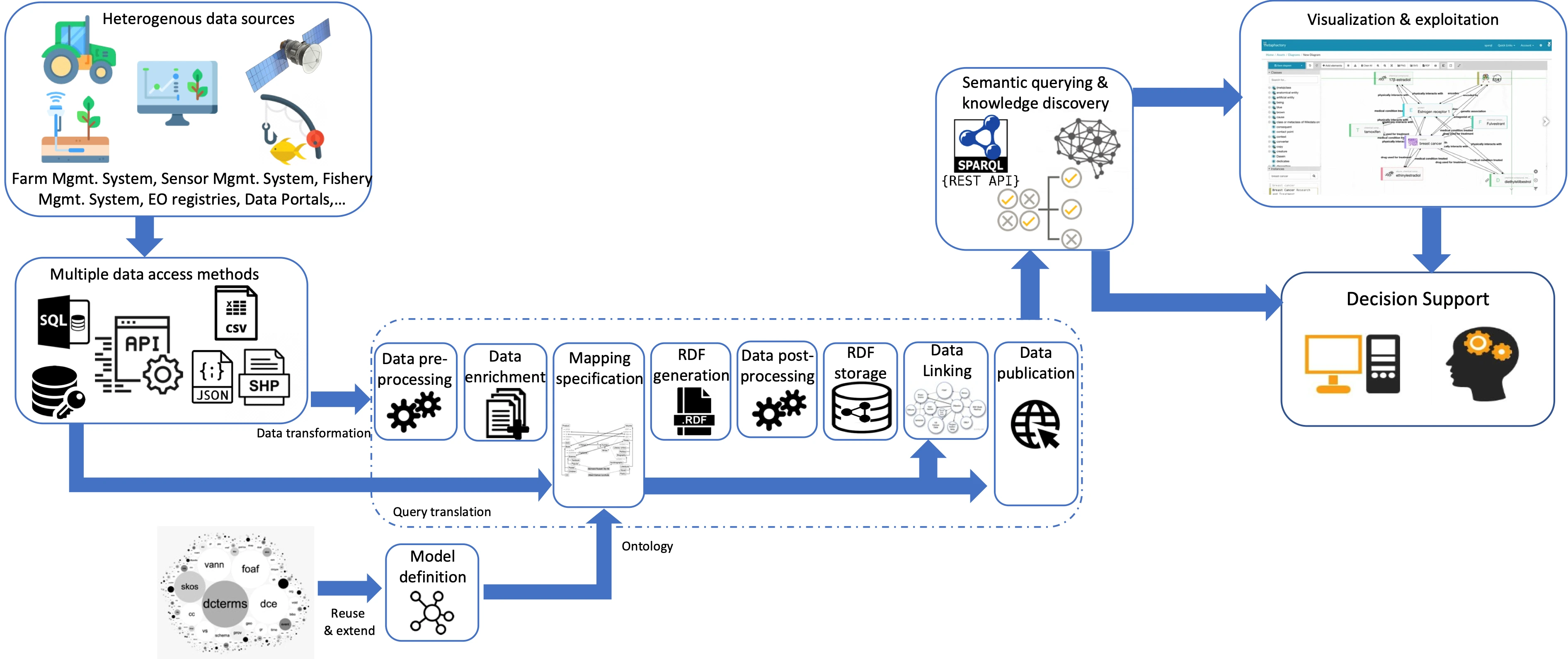
How can the service help you?
Data harmonisation will enable customer
-enhanced interoperability between different systems, machines, and software platforms by making data consistent, standardised, and easily exchangeable across various technologies.
Harmonised data:
- ensures that different systems can communicate by using a common data format
- Support the connection of legacy systems with modern platforms, allowing businesses to adopt new technologies without discarding existing infrastructure.
-enables IoT devices, agro-robots, and other smart systems to share data in real time, improving automation and efficiency.
- facilitates interoperability between different sectors, such as agriculture and manufacturing, by ensuring data can be used across multiple domains.
- helps businesses meet industry standards and legal requirements, reducing risks and improving data governance.
- enables an integrated view and access of data coming from different sources, for instance, by data analytics components and decision support systems to leverage the full value of all available data Data harmonisation acts as a "universal translator" that enables different systems and machines to work together smoothly, making processes more efficient, automated, and future-proof.
How the service will be delivered
Remotely as a cloud service, for instance, in a scenario requiring a service that transforms agricultural data from different IoT devices into a standard format (e.g., AIM). It can also be provided as an on-premise deployment where a customer integrates the service into its internal system to standardise machine data with the support of a data engineer, or as a CLI tool (deployed via Dockerfile), which can be easily integrated into internal systems. Additionally, the customer will receive mappings of the dataset(s) identified and target data model (e.g., AIM) and the pipeline definitions to carry out the harmonisation.
Service customisation
The service can be customised to fulfil particular customers’s needs. The processing of the service typically involves the specification of custom mappings for specific data sources, which would also be provided. Additionally, in many cases, the service will need to be customised to integrate it within a data processing module in the customer’s own systems.